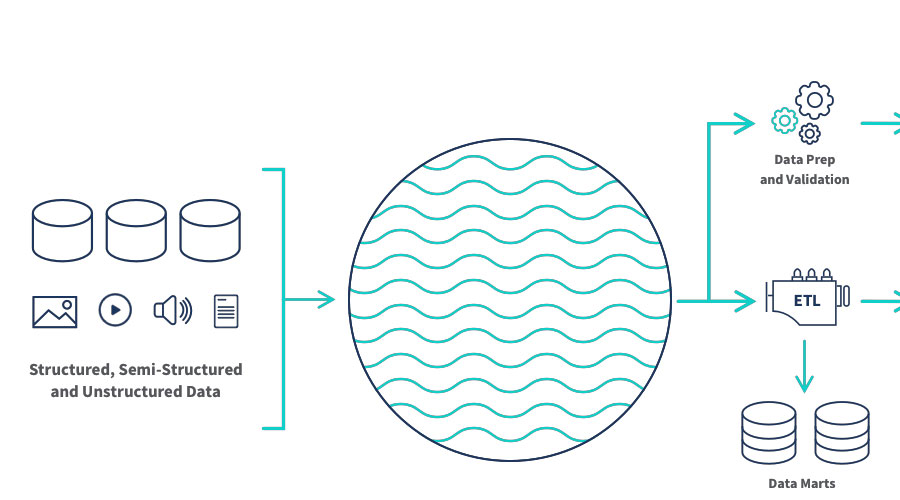
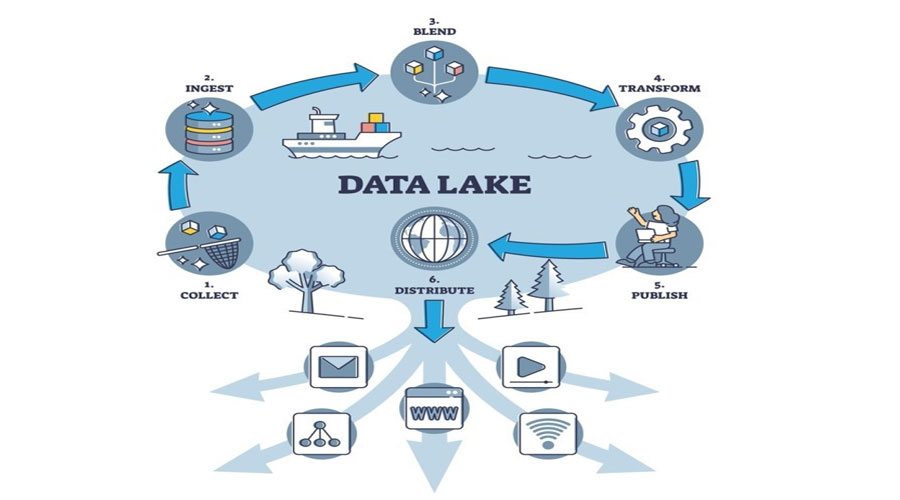
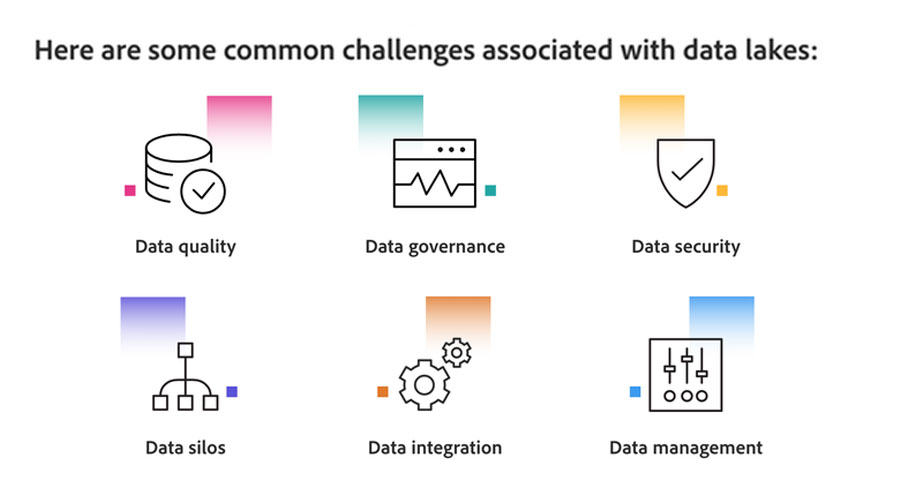
Today's highly connected, insights-driven world would not be possible without the advent of data lake solutions. That's because organizations rely on comprehensive data lakes platforms, such as Azure Data Lake, to keep raw data consolidated, integrated, secure, and accessible. Scalable storage tools like Azure Data Lake Storage can hold and protect data in one central place, eliminating silos at an optimal cost. This lays the foundation for users to perform a wide variety of workload categories, such as big data processing, SQL queries, text mining, streaming analytics, and machine learning. The data can then be used to feed upstream data visualization & reporting needs. A modern, end-to-end data platform like Azure Synapse Analytics addresses the complete needs of a big data architecture centered around the data lake.